Discover the Causes, Triggers, and Treatment Options
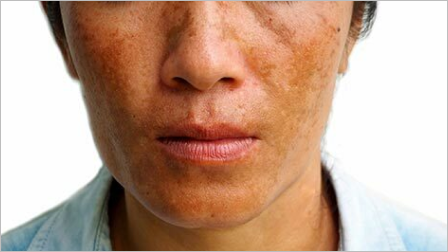
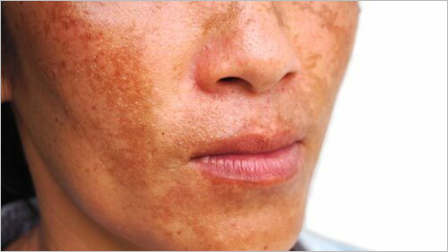
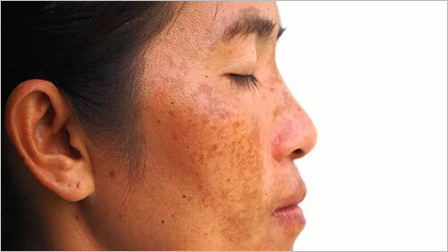
Melasma is a hyperpigmentation disorder that causes dark, discolored patches on the skin. These patches typically appear on areas of the face exposed to the sun, such as the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. Melasma affects both men and women, but it is more common in women, especially during pregnancy (known as chloasma or the “mask of pregnancy”). Hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetic factors contribute to the development of melasma
Hormonal changes play a significant role in melasma development. Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy or while taking oral contraceptives, can trigger melasma. Sun exposure is another crucial factor, as ultraviolet (UV) radiation stimulates the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Genetic factors also play a role, as individuals with a family history of melasma are more prone to developing the condition. Other triggers include certain medications, hormonal imbalances, and thyroid disorders.
The most common areas for melasma to appear on the face include:
Melasma may also appear on other areas of the body, especially those exposed to a lot of sunlight. These areas may include:
Diagnosing melasma is usually based on a visual examination of the affected skin. A dermatologist may inquire about the patient’s medical history, including any hormonal changes, sun exposure habits, or family history of melasma. It is essential to differentiate melasma from other skin conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, lentigo, or certain fungal infections. Biopsies or additional tests may be necessary to rule out other potential causes
Diagnosing melasma is usually based on a visual examination of the affected skin. A dermatologist may inquire about the patient’s medical history, including any hormonal changes, sun exposure habits, or family history of melasma. It is essential to differentiate melasma from other skin conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, lentigo, or certain fungal infections. Biopsies or additional tests may be necessary to rule out other potential causes

Sun Protection
One of the most crucial aspects of melasma management is protecting the skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays. This includes wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing and accessories.

Various topical creams and lotions may be prescribed to lighten the melasma patches. These treatments often contain ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, corticosteroids, or azelaic acid, which work by reducing melanin production and promoting cell turnover

Chemical Peels
Dermatological procedures such as chemical peels can help improve melasma by exfoliating the outermost layers of the skin. Different types of peels, such as glycolic acid or trichloroacetic acid peels, may be used depending on the severity of the condition.

Microdermabrasion
This procedure involves gently exfoliating the skin using a handheld device. Microdermabrasion helps remove the outer layer of skin cells, promoting skin rejuvenation and reducing the appearance of melasma.

Laser Therapy
Certain laser treatments, such as fractional laser resurfacing or intense pulsed light (IPL), can target melasma pigmentation and stimulate collagen production. These treatments are usually performed by dermatologists or skincare professionals

Over-the-counter drugs or supplements
Some oral supplements may support skin health and help manage melasma. Antioxidant-rich supplements like vitamin E, vitamin C, and green tea extract can provide additional protection against sun damage and promote overall skin health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, may also have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit the skin.
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies may help manage melasma. These include maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, managing stress levels, avoiding excessive sun exposure, and using natural remedies like aloe vera, vitamin C serums, or licorice extract.



Melasma can have a significant impact on a person’s self-image and mental well-being. It is crucial to address the emotional aspect of living with melasma. Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can provide a sense of understanding and community. Practicing self-care, engaging in activities that boost self-confidence, and seeking professional help if needed can also aid in coping with the psychological impact of melasma.
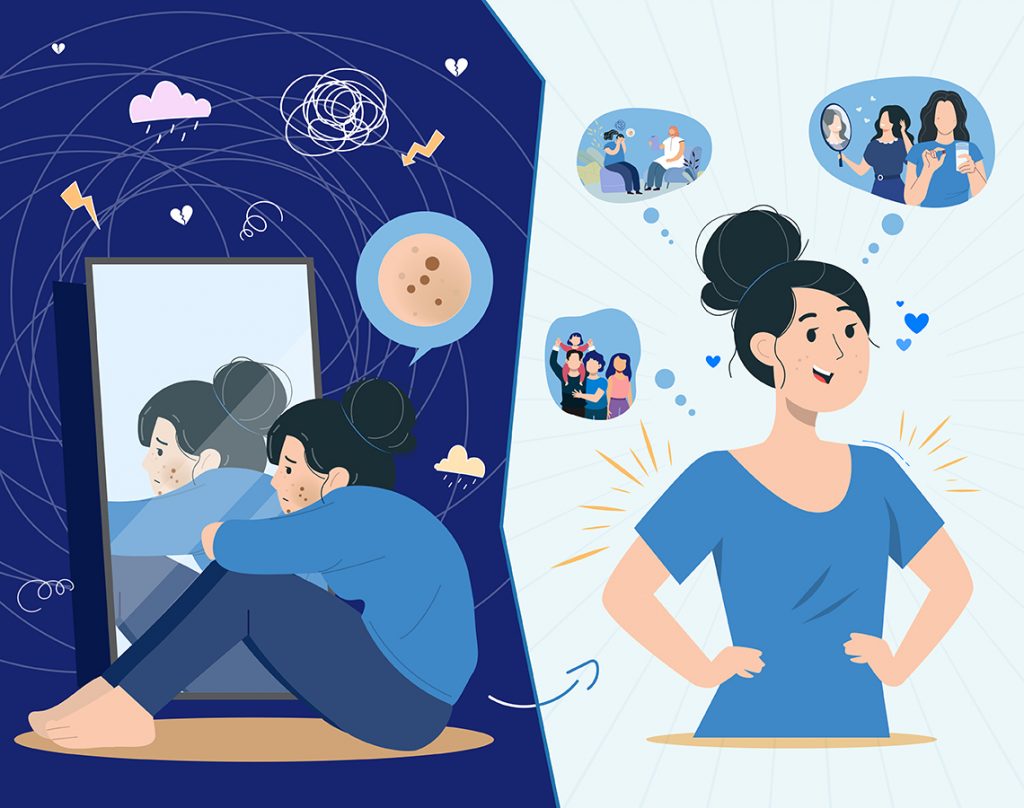

Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by the appearance of dark patches on the face. Although it may be challenging to manage, understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options can help individuals effectively reduce the appearance of melasma. By combining medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and home remedies, individuals can regain confidence and achieve clearer, more even-toned skin. Remember to consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Mega Lifesciences Limited Inc. is actively involved in helping Filipinos have access to safe, effective, and world-class quality supplements, over-the-counter, and ethical products.
Signup for access to special offers, new products, tips, and more.
© Copyright 2026 Pynocare, All Rights Reserved